Fiber Optic Frequently Asked Questions
General Questions
What is the Fiber Optic?
Fiber optic cables are made of glass or plastic. Glass fiber is stronger and more durable but plastic is much easier to work with. Plastic is also cheaper. Fiber-optic cables are thin and do not need a lot of room order to transmit data over long distances. They are also more immune to interference than other cables because they use light rather than radio waves or electricity to carry data across the network, which means they do not require protective shielding like other types of cables do.
Fiber cables vary enormously, in the type of fiber, the construction and materials, and the number of fibers present. Optical fibers are extremely thin strands of very high purity silica (glass), which transmit light from one end to the other with minimal loss.
Why is Fiber optic cables better than copper?
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables over Copper Cables:
1. Greater Bandwidth
- Faster Speeds
- Longer Distances
- Better Reliability
- Thinner and Sturdier
- More Flexibility for the longer term
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership
How Does Weather Impact Fiber Optics?
Is Fiber optic faster than 4G and 5G?
Does fiber optic cable have to be in conduit?
Technical Questions
Fiber Optic Types
Multimode fiber can carry multiple light rays (modes) at an equivalent time by having varying optical properties at the core; essentially light traveling the shortest path (down the middle) travels the slowest. The larger core simplifies connections and takes advantage of the lower-cost LED & VCSEL technologies which operate within the 850nm window. Due to dispersion, the range is restricted so it tends to be used as premises cabling when less than a kilometer. It comes in two core sizes, 62.5 and 50 microns.
Single-mode fiber features a much smaller core size of 9 microns and features a single light path and may travel for much longer distances of up to 100km. These require costlier electronics that operate within the 1310 and 1550nm windows and are typically utilized in long-distance LANs, Cable TV, and telephony applications.

What is the difference between multimode and single mode fiber (fibre) optic cable?
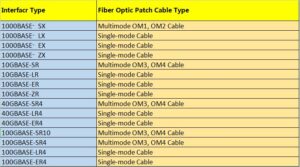
Fiber Optic Cable Transmission Distances
The table below shows distances for ratified standards only.

The Difference Between OM1,OM2,OM3, OM4 and OM5 Multimode Fibers
- Color – Orange
- Core Size – 62.5um
- Data Rate – 1GB @ 850nm
- Distance – Up to 300 meters
- Applications – Short-Haul Networks, Local Area Networks (LANs) & Private Networks
- Color – Orange
- Core Size – 50um
- Data Rate – 1GB @ 850nm
- Distance – Up to 600 meters
- Generally used for shorter distances • 2x Distance Capacity of OM1
- Applications – Short-Haul Networks, Local Area Networks (LANs) & Private Networks
OM3 – laser-optimized Multimode
- Color – Aqua
- Core Size – 50um
- Date Rate – 10GB @ 850nm
- Distance – Up to 300 meters
- Uses fewer modes of light, enabling increased speeds
- Able to run 40GB or 100GB up to 100 meters utilizing an MPO connector
- Applications – Larger Private Networks
OM4 – laser-optimized Multimode
- Color – Aqua
- Core Size – 50um
- Data Rate – 40GB up to 100GB@ 850nm
- Distance – Up to 550 meters
- Able to run 100GB up to 150 meters utilizing an MPO connector
- Applications – High-Speed Networks – Data Centers, Financial Centers & Corporate Campuses
OM5 is the first approved as WBMMF (Wide Band Multimode Fiber) is designed to specifically handle high-speed data center applications using two fibers to transmit from 40GBs up to 100GBs and is powered by shortwave wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM).
- Color – Limegreen
- Core Size – 50um
- Data Rate – 40GB up to 100GB @ 850nm to 953nm
- Distance – Up to 440 meters @40Gb and Up to 150 meters @100GB
Ordering Questions
How do I order fiber optic products from iFiber Optix?
You can browse our selection online and place an order through our store or contact us directly for custom quotes.
